HUE Integration
This document describes the procedures needed to integrate HUE Native with WorksAudit.
Following are the general steps to integrate HUE Native with WorksAudit:
- Configure WorksAudit environment to authorize HUE Native’s Lambda and Firehose to write to S3. See section 1.2 for details.
- Get HUE Native configuration values from WorksAudit environment. See 1.3 for details.
- Configure HUE Native
environment-setup-scriptto prepare it for WorksAudit integration initialization. See 1.4 for details. - Run WorksAudit initialization playbook in the target HUE environment. See 1.5 for details.
- Confirm that all necessary AWS resources are created properly in HUE environment/HUE AWS Account. See 1,6 for details.
- Configure IdP (HUE, or other IdP side). See here for details.
- Configure SP (WorksAudit side). See here for details.
- Confirm that a user can login to WorksAudit through HUE-IdP.
TODO: write procedure to setup Firehose, etc.
Notes: for development environments (dev and eva) this task is the responsibility of Audit team, for commercial environments (stg and pro) this task is the responsibility of BAP SRE team.
Relevant HUE Native resources (legacy raw log synchronization lambda and Kinesis Firehose for RDBClient) needs to have access to target WorksAudit’s central S3 bucket. The steps to grant permission to HUE Native resources are as follow:
- Get the AWS Account ID (12-digit) that hosts HUE Native environment to be granted, e.g.
123456789012 - Use this utility and run the
add_new_accounts_to_bucket_policytask to register the account in WorksAudit environment.
Notes: for development environments (dev and eva) this task is the responsibility of Audit team, for commercial environments (stg and pro) this task is the responsibility of BAP SRE team.
Following are the variables that needs to be obtained from WorksAudit AWS account that hosts the target environment:
| Variable Name | Meaning and Purpose | How to Obtain | Where to Set |
|---|---|---|---|
WORKSAUDIT_CLIENT_ID |
Client ID for authority and multilingual data sync EDP2 batch to access WorksAudit services. | See section 1.3.1 below. | tenant-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_CLIENT_SECRET |
Client secret for authority and multilingual data sync EDP2 batch to access WorksAudit services. | See section 1.3.1 below. | tenant-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_AUTHENTICATION_ENDPOINT |
Endpoint for authenticating client to WorksAudit | Static value depending on the environment: https://hue-worksaudit-{environment}.auth.ap-northeast-1.amazoncognito.com/oauth2/token?grant_type=client_credentials. Replace {environment} with the environment name. For example, for stg the value would be https://hue-worksaudit-stg.auth.ap-northeast-1.amazoncognito.com/oauth2/token?grant_type=client_credentials |
tenant-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_PRESIGNED_URL_GENERATOR_ENDPOINT |
Endpoint of the service to generate presigned URL to upload to WorksAudit’s target bucket. | Static value depending on the environment: https://api.{environment}.audit.worksap.com/ref/presignedurl. Replace {environment} with the environment name. For example, for stg the value would be https://api.stg.audit.worksap.com/ref/presignedurl |
tenant-config.yml |
Following are other variables that the values are generated or static and can be determined by knowing what target WorksAudit environment to be integrated with (replace {environment} with the target environment name, e.g. stg)
| Variable Name | Meaning and Purpose | Value | How/Where to Set |
|---|---|---|---|
WORKSAUDIT_ENVIRONMENT |
Specifies the WorksAudit target environment | One of the following: man, dev, eva, stg, pro |
Generated |
WORKSAUDIT_SUBDOMAIN |
Specifies the WorksAudit subdomain of worksap.com |
For man, dev, eva it should be audit-dev. For stg, pro it should be audit. |
Generated |
HUE_WORKSAUDIT_PIPELINE_FIREHOSE_NAME |
Name of Kinesis Firehose to be created in the HUE AWS account. This Firehose is used by HUE to stream protobuf audit log data to WorksAudit central bucket. | wap-audit-pipeline-{aws-account-id}-{environment} where:{aws-account-id} is the12-digit AWS account id where the HUE environment is hosted. |
Generated |
WORKSAUDIT_CENTRAL_S3_BUCKET_NAME |
Name of the WorksAudit central bucket name specific to target environment. | Constant: wap-audit-central-{environment} |
common-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_SHIPMENT_S3_BUCKET_NAME |
WorksAudit shipment bucket where the released artifacts are distributed. | Constant for all environments: wap-audit-shipment |
common-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_SHIPMENT_S3_ACCESS_KEY_ID |
Access key to WorksAudit shipment bucket. | Constant for all environments (ask Audit team to provide the value). | common-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_SHIPMENT_S3_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY |
Secret key to access WorksAudit shipment bucket. | Constant for all environments (ask Audit team to provide the value). | common-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_SHIPMENT_S3_REGION |
Region of WorksAudit shipment bucket. | Constant for all environments: ap-northeast-1 |
common-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_LOG_SYNC_LAMBDA_NAME |
Name of the lambda for copying HUE native log to WorksAudit central bucket. | Constant for all environments: hue-worksaudit-lambda-log-sync |
common-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_LOG_SYNC_LAMBDA_VERSION |
Version of the lambda for copying HUE native log to WorksAudit central bucket. | Constant for all environments: 1.0.0 |
common-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_LOG_FILTER_LAMBDA_NAME |
Name of the lambda for filtering logs in WorksAudit Firehose. | Constant for all environments: hue-worksaudit-lambda-firehose-batch-filter |
common-config.yml |
WORKSAUDIT_LOG_FILTER_LAMBDA_VERSION |
Version of the lambda for filtering logs in WorksAudit Firehose. | Constant for all environments: 1.0.0 |
common-config.yml |
For an example of the files with the values above set for bapfbt/develop environment, see:
- http://product-ci/tools/environment-config/blob/develop/bapfbt/vars/tenant-config.yml#L92-98
- http://product-ci.workslan/tools/environment-config/blob/develop/all-tenants-config/bapfbt-common-config.yml
here.
Following are the steps to get the client ID and secret required to configure HUE:
- Open the AWS console with your account.
- Go to Cognito.
- Find and open the user pool for the target environment:
wap-audit-cognito-user-pool-hue-{environment}. Replace{environment}with the name of the target environment. For example, forstgenvironment the user pool would bewap-audit-cognito-user-pool-hue-stg. - On the left hand side panel. Click
App clients. - Create a new App client. Name it as common-common (means all HUE tenants share the same app client, you can also name it as another name). Leave other settings as default and create the app client. See following image:
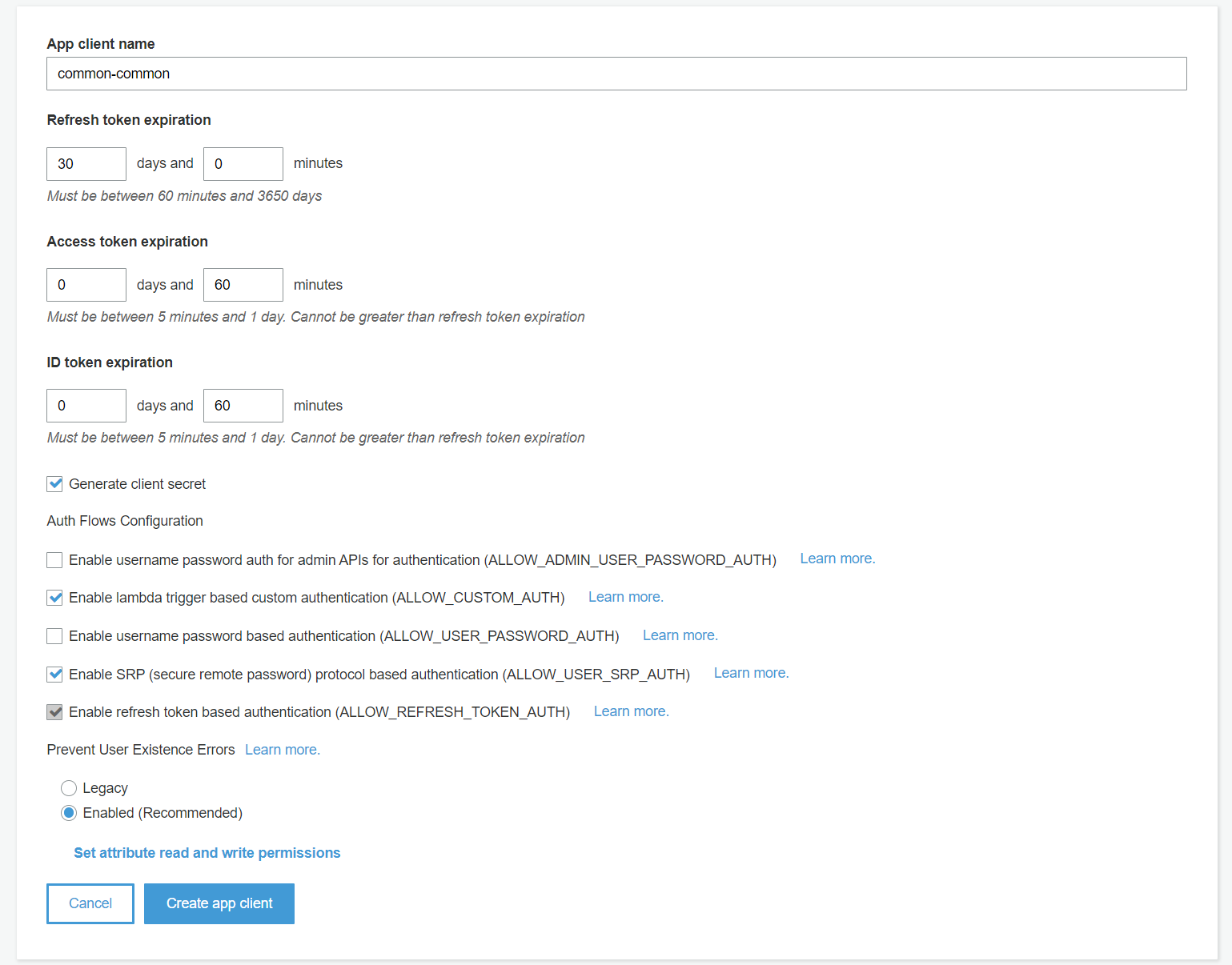
- Click on
App client settingson the left hand side panel. Then find the app client you created just now. In the OAuth 2.0 section, tick theClient credentialsoption and theapi.{environment}.audit.worksap.com/authority_write(replaceenvironentwith the name of the target environment, e.g.stg) under theAllowed Custom Scopessub-section. See following image: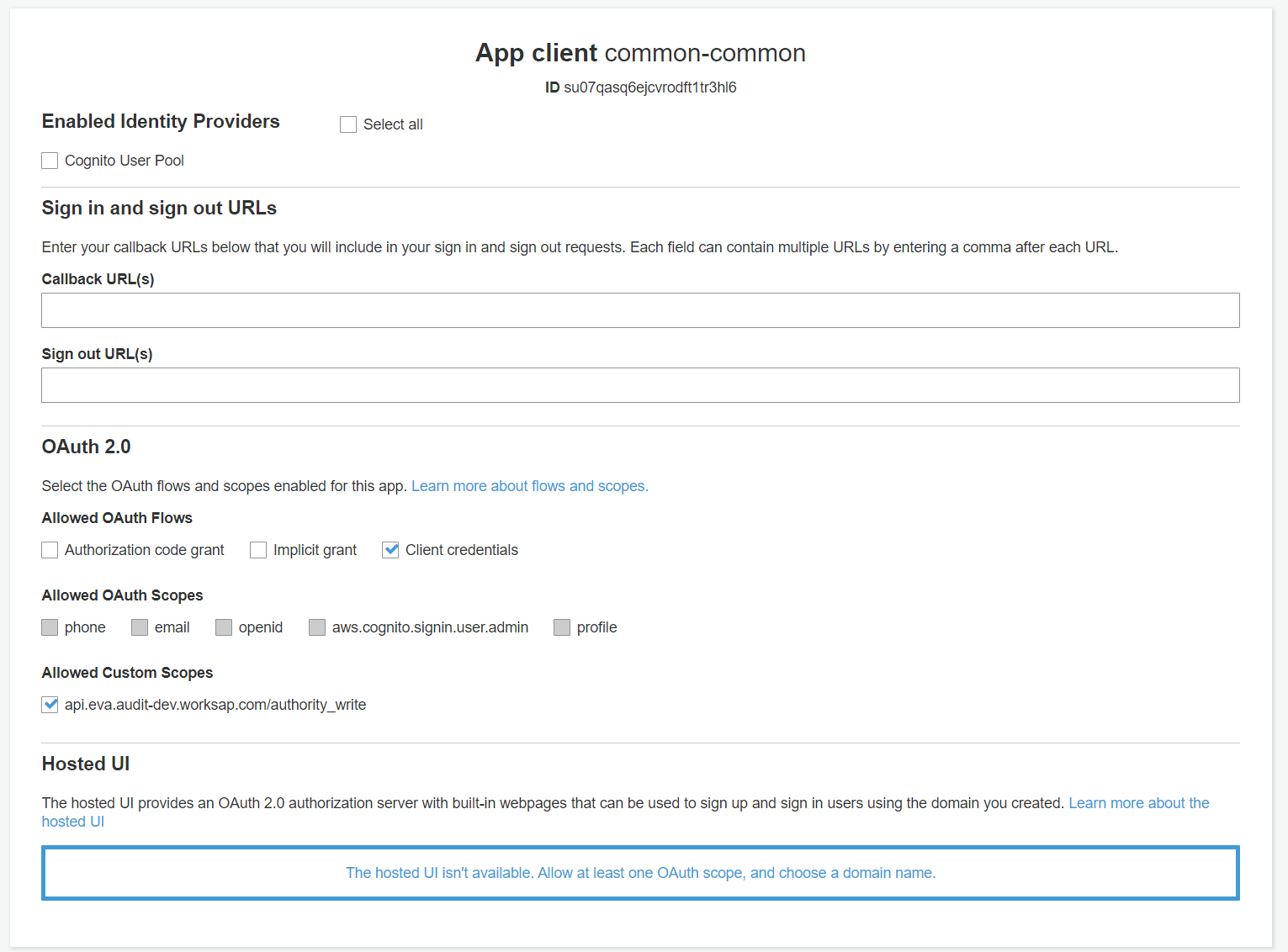
- Click the
App clienton the left hand side panel and find the app client you created. Expand it and find the two values:App client idandApp client secret. The first one is theWORKSAUDIT_CLIENT_IDand the second one isWORKSAUDIT_CLIENT_SECRET. See following image: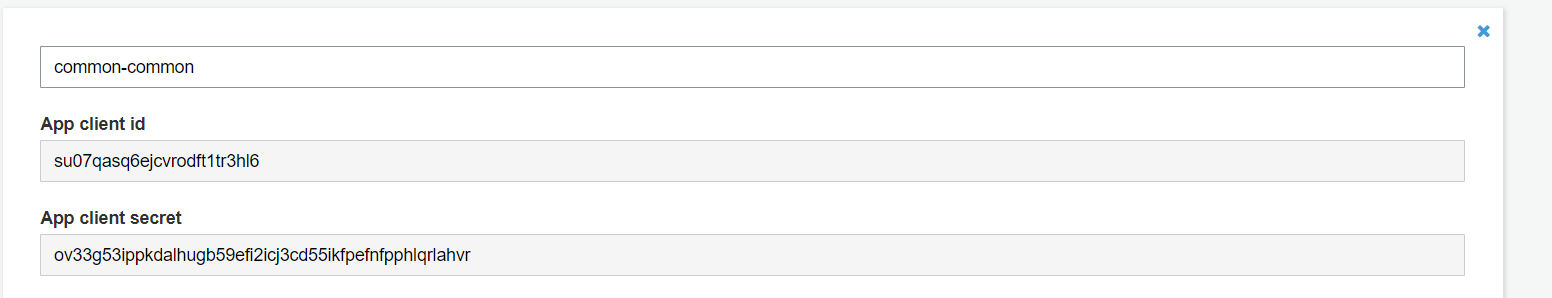
Notes: Generally this task is the responsibility of SCM SRE team. On some internal environments, developers may have permission to do this task by themselves.
There are usually two ways to apply the values as described in the previous section in environment-setup-script:
- Run a Jenkins job to execute
generate-main-yamlscript. This script will generatesmain.ymlrequired to run playbooks. - Edit
main.ymlmanually.
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/18dbSzOChelPQx93CYVcwwxpOFyVl3VUWJEBSz_lcWEM/edit#gid=0
Notes: Generally this task is the responsibility of SCM SRE team. On some internal environments, developers may have permission to do this task by themselves.
Before execution, make sure that you are using an appropriate branch of environment-setup-script that has:
initialize-worksauditplaybook defined.- Make sure that the variables required for this playbook is provided in the
environment-config. See following example forbapfbt/developenvironment. - Make sure that the playbook is executed without error.
- Make sure that the variables required for this playbook is provided in the
- Updates related to
nginxredirect for WorksAudit HUE Menu. - Updates related to HUE authority, user, and multilingual data synchronization from HUE to WorksAudit.
- Updates related to Kinesis Firehose creation for WorksAudit producer to be able to stream logs from HUE.
- Updates related to fix to the problem with permission to create Firehose.
The procedures that is required to apply the integration are:
| Step | Playbook | Purpose | Node to Run |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | execute-update-config |
For updating HUE’s application.properties so that the values in the configuration are being picked-up by APs/batches. |
Single WT |
| 2 | kubernetes-unified-k8s-update-ingress-controller |
For updating HUE’s nginx rules so that link in the WorksAudit menu can be redirected correctly. | Common WT |
| 3 | initialize-worksaudit |
Main WorksAudit integration script that will creates all AWS resources necessary for WorksAudit integration. | Single WT |
Use this Assert Environment Tool to check and confirm that HUE on a certain tenant/landscape has been configured properly to integrate with WorksAudit on a certain environment.
Alternatively, you can also do following steps manually:
-
Check if a Lambda named
hue-worksaudit-lambda-log-sync-{tenant}-{landscape}exists in the AWS account that hosts the HUE environment. Replace{tenant}with the tenant name, and{landscape}with landscape name of the HUE being investigated. For example, you can run following command to check the lambda for tenantbapfbtand landscapedevelop:aws lambda get-function --function-name hue-worksaudit-lambda-log-sync-bapfbt-develop -
Check if the lambda has policy to let an S3 bucket invoke the function. For example, you can run following command to check the lambda for tenant
bapfbtand landscapedevelop:aws lambda get-policy --function-name hue-worksaudit-lambda-log-sync-bapfbt-develop --query Policy --output textThis command will produce a JSON that looks something like:
{"Version":"2012-10-17","Id":"default","Statement":[{"Sid":"hueWAAllowLmbLogSyncFromS3","Effect":"Allow","Principal":{"Service":"s3.amazonaws.com"},"Action":"lambda:InvokeFunction","Resource":"arn:aws:lambda:ap-northeast-1:309514382466:function:hue-worksaudit-lambda-log-sync-bapfbt-develop","Condition":{"ArnLike":{"AWS:SourceArn":"arn:aws:s3:::huelog-eva-scmci"}}},{"Sid":"hueWAAllowLmbLogSyncFromS3_bapfbt_develop","Effect":"Allow","Principal":{"Service":"s3.amazonaws.com"},"Action":"lambda:InvokeFunction","Resource":"arn:aws:lambda:ap-northeast-1:309514382466:function:hue-worksaudit-lambda-log-sync-bapfbt-develop","Condition":{"ArnLike":{"AWS:SourceArn":"arn:aws:s3:::huelog-eva-scmci"}}}]}At the end of the JSON, there should be an ARN of HUE log’s bucket used by current tenant and landscape:
"AWS:SourceArn":"arn:aws:s3:::huelog-eva-scmci" -
Check if the bucket found in the previous step has configuration to trigger the lambda in step (1). Run following command:
aws s3api get-bucket-notification-configuration --bucket huelog-eva-scmciThis command should output a list of notifications. One of them should trigger the lambda for tenant
bapfbtand landscapedevelop. There should be a part that looks like:"LambdaFunctionArn": "arn:aws:lambda:ap-northeast-1:309514382466:function:hue-worksaudit-lambda-log-sync-bapfbt-develop" -
Check if the Kinesis Firehose is created correctly. Run following command:
aws firehose list-delivery-streamThis command should output the name of the Firehose created. Make sure that it matches with the name defined in
HUE_WORKSAUDIT_PIPELINE_FIREHOSE_NAME.
Following are the Slack threads on the HUE integration works:
- HUE
ki4g/productionwith WorksAuditpro(2020/8/19). There are many threads related to this integration:#env_audit:- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CQZMQKU5U/p1597803730192700
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CQZMQKU5U/p1597887721232600
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CQZMQKU5U/p1597920592013500
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CQZMQKU5U/p1598328148018400
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CQZMQKU5U/p1598437940065200
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CQZMQKU5U/p1598518970068500
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CQZMQKU5U/p1598523614071600
#env_scm_staging:- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CEH822LDV/p1597895887005300
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CEH822LDV/p1597971960023300
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CEH822LDV/p1597991432029100
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CEH822LDV/p1598337197076000
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CEH822LDV/p1598508817012700
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CEH822LDV/p1598628213106100
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CEH822LDV/p1598650671141700
#topic_kajima_infra_test- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CUKURJFPY/p1598428648046100
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CUKURJFPY/p1598436970057500
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CUKURJFPY/p1598495354087900
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CUKURJFPY/p1598588460124400
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CUKURJFPY/p1598656551150700
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CUKURJFPY/p1598684063207900
- https://worksap-ws.slack.com/archives/CUKURJFPY/p1598684414208700
- HUE
ki4g/ex96with WorksAuditstg(2021/1/14). - HUE
ki4g/ex92with WorksAuditstg(2021/1/20).